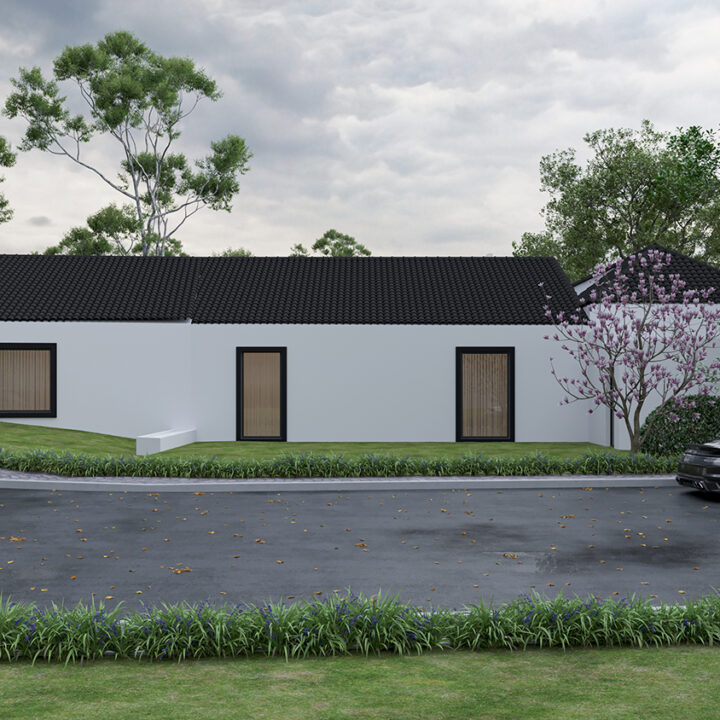
Exterior
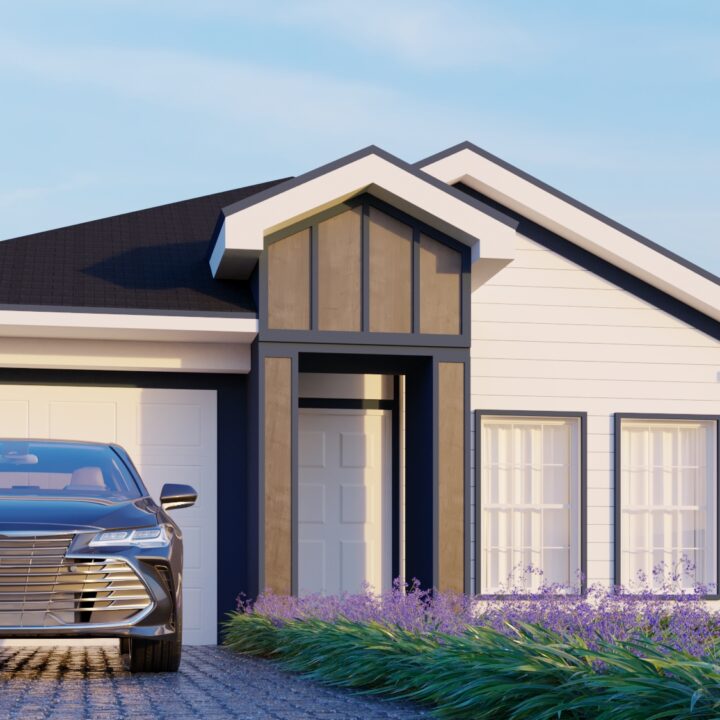
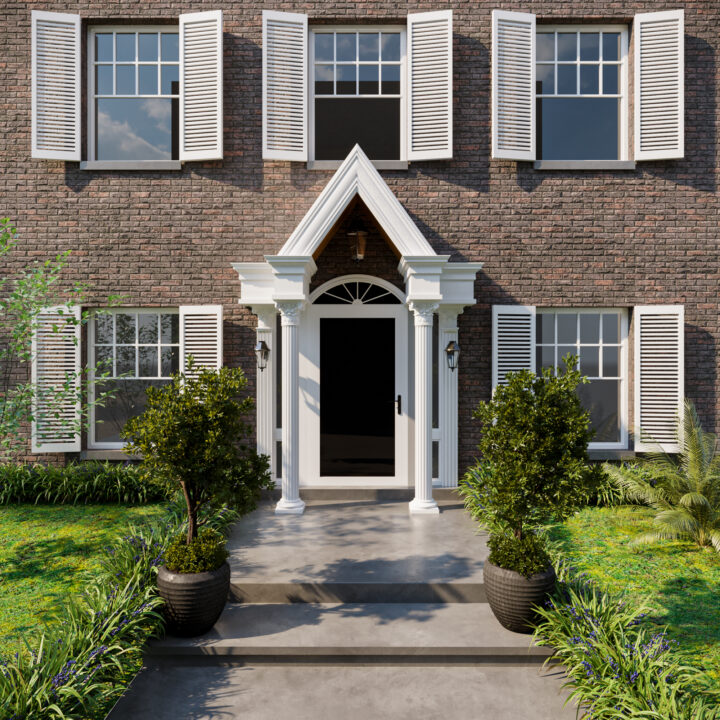
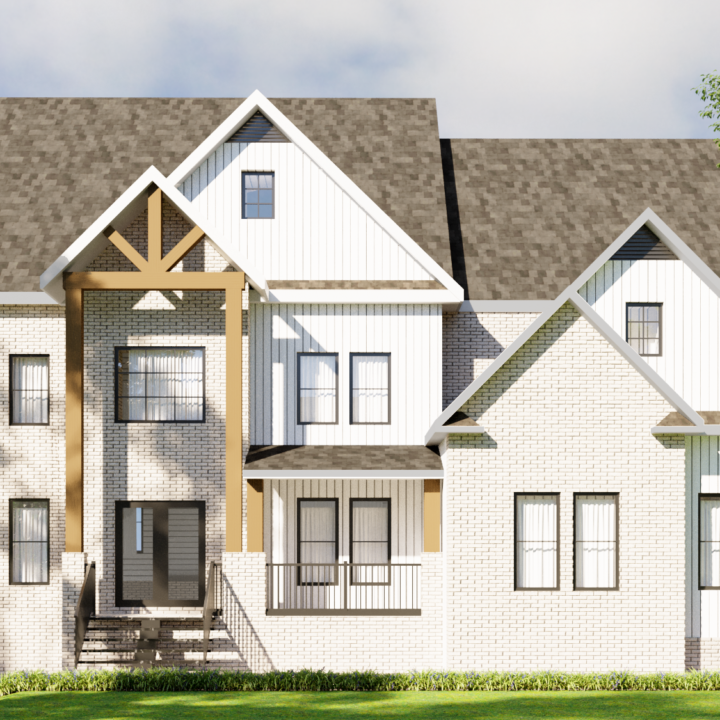
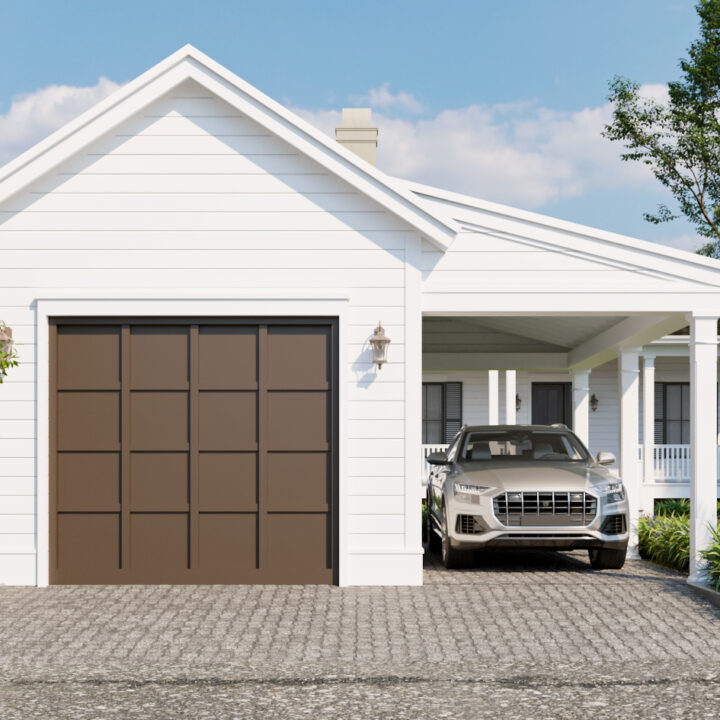
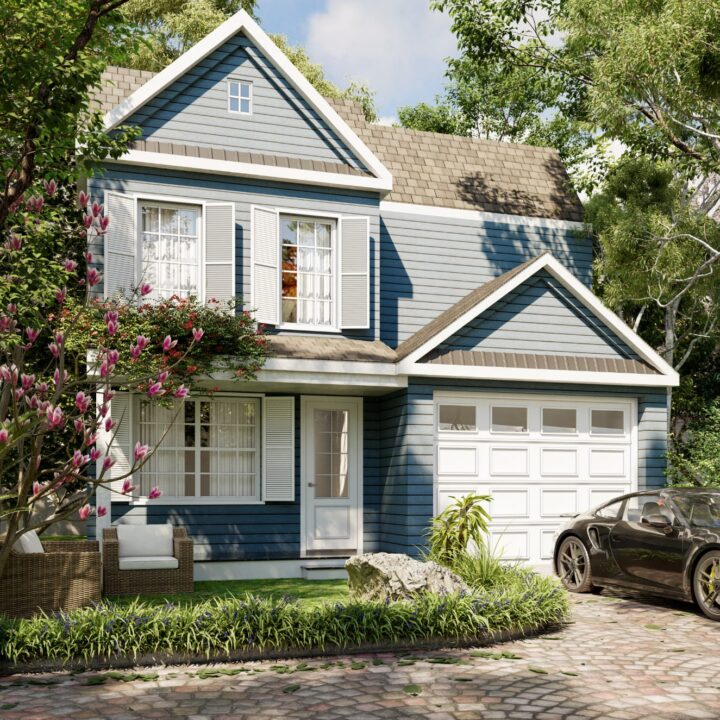
Exterior Architecture refers to the design and planning of the external elements of a building or structure, including its façade, landscaping, and surrounding environment. This discipline combines aesthetics, functionality, and structural integrity to create an inviting and effective exterior that complements the overall design while meeting practical needs.
From residential homes to commercial complexes, exterior architecture is crucial for shaping how a building interacts with its environment and how it is perceived by the public. It involves thoughtful design choices regarding materials, shapes, and how the structure integrates with the surrounding landscape or urban setting.
Key Elements of Exterior Architecture:
✔ Façade Design – The front or face of the building, often featuring architectural details such as windows, doors, and decorative elements.
✔ Landscaping & Green Spaces – Gardens, paths, and outdoor living areas that enhance the building’s aesthetic and environmental impact.
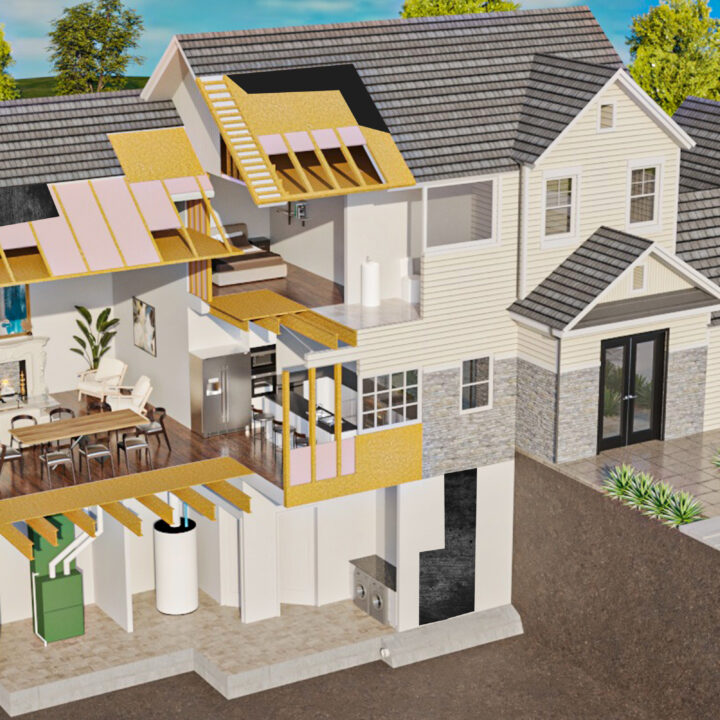
✔ Building Materials – Choosing materials such as brick, stone, glass, or wood that provide both beauty and durability for the exterior.
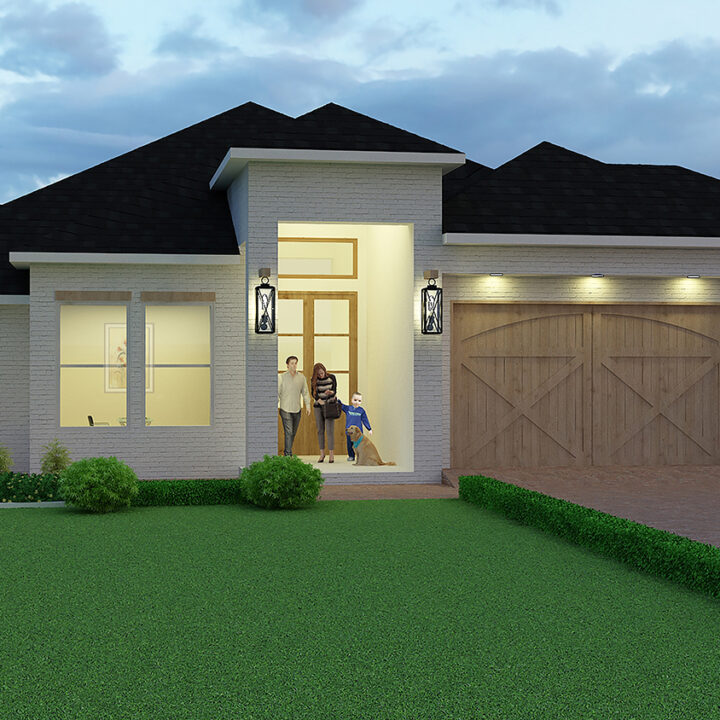
✔ Lighting & External Features – Strategically placed outdoor lighting, signage, and other elements that highlight key features and ensure functionality after dark.
✔ Environmental Integration – Designing exteriors that complement or enhance the surrounding environment, whether urban, suburban, or rural.
Uses of Exterior Architecture:
📌 Residential Projects – Designing exterior spaces for homes that are both functional and visually appealing.
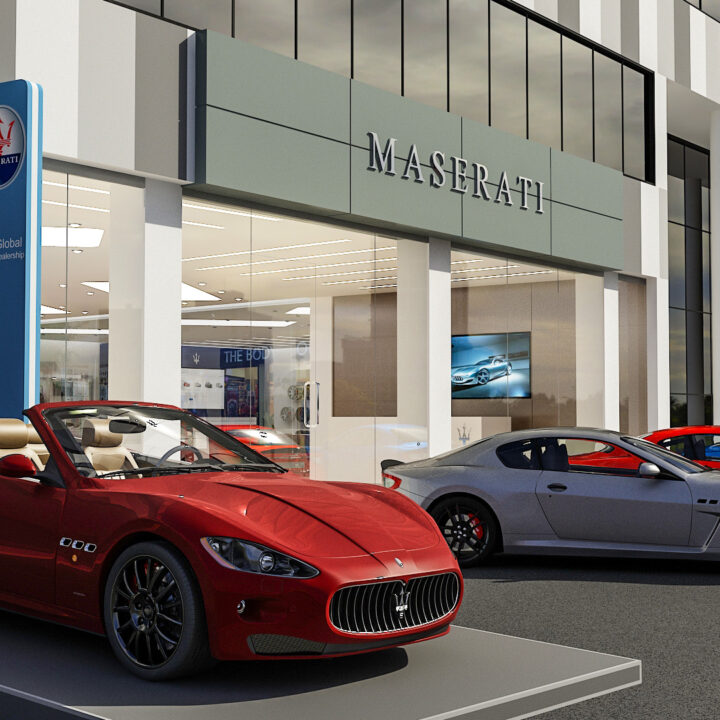
📌 Commercial Developments – Creating professional, eye-catching façades and public spaces that attract customers or clients.
📌 Urban Planning – Enhancing streetscapes and public areas to promote sustainability and community engagement.
📌 Historical & Preservation Work – Restoring or preserving exterior elements of historic buildings while maintaining their heritage.